Formal
Algorithm
Common
Docker
Javascript
Network
Node
Notes
c++
c++Lib
golang
Javascript
Webpack
Vite
Webassembly
MCU
Protocol
ML
Compilation
DataStructure
Algorithm
MC_MP_Programming
ResearchMethod
PrivacySecurity
EfficientAlgorithm
AdvancedAlgorithmicTech
AlgorithmGameTheory
LowCodeProject
ComputerCompose
Network
LinearMath
OperationSystem
Mathmatic
Multiple Features (variables)
-
Previously: f<w, b>(x) = wx + b
-
Now: f<w, b>(x) = w1x1 + w2x2 + w3x3 + w4x4 + … + wnxn + b (Multiple Linear Regression)
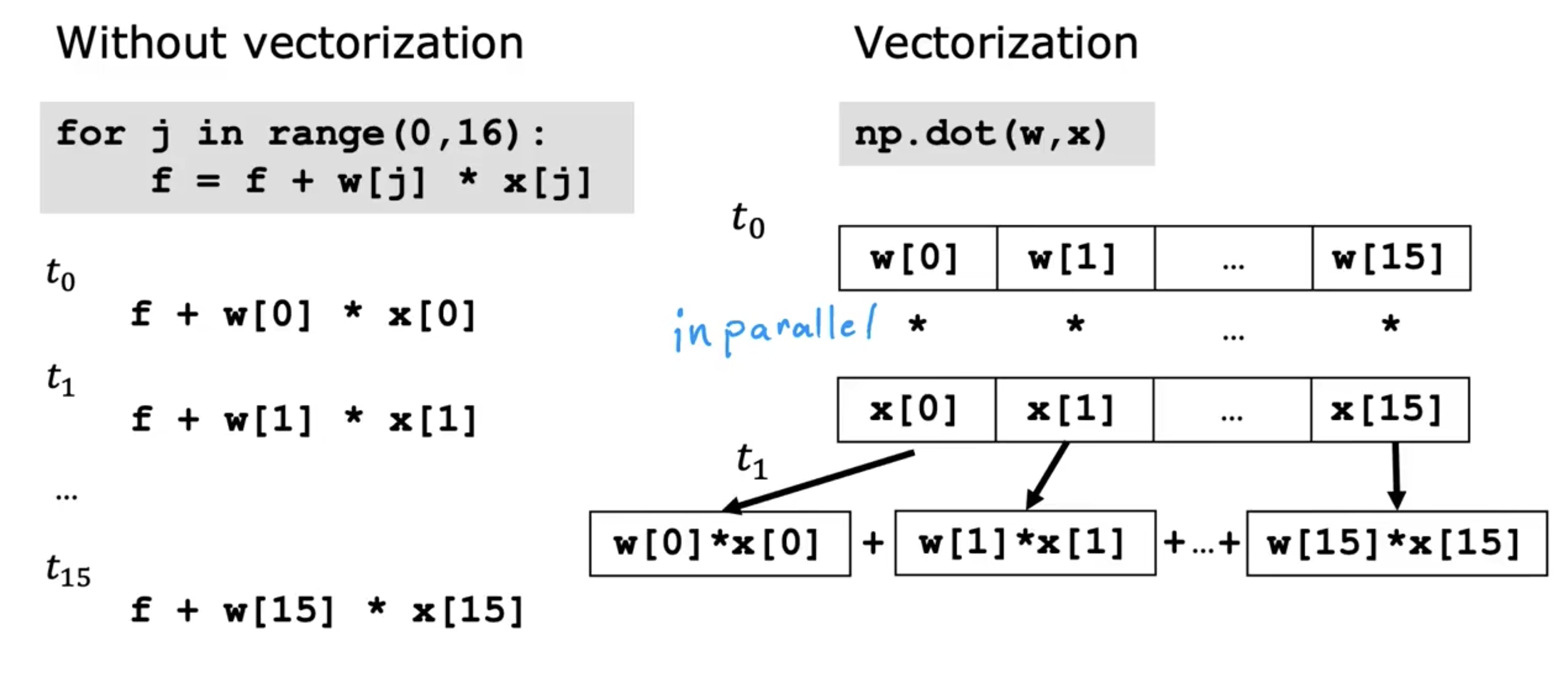
Vectorization
Using vectorization will both make your code shorter and also make it run more efficiently
Vectorization how to work on our computer
Gradient descent for multiple regression
if 300 <= x_1 <= 2000
x_1, scaled = x_1 / 2000 (max)
0.15 (300 / 2000) <= x_1, scaled <= 1 (2000 / 2000)
Feature scaling
Mean Normalization
if you want to calaulate the mean normalization. first of all, you have to calculate the average (x1 on your training set), which is called Mu_1.
x_1 = x_1 - Mu_1 / Max - Min
For example Mu_1 = 600, 300 <= x_1 <= 2000, so -0.18 (300 - 600) / (2000 - 300) <= x_1 <= 0.82 (2000 - 600) / (2000 - 300)
Z-scope Normalization
Starndard deviation
