Formal
Algorithm
Common
Docker
Javascript
Network
Node
Notes
c++
c++Lib
golang
Javascript
Webpack
Vite
Webassembly
MCU
Protocol
ML
Compilation
DataStructure
Algorithm
MC_MP_Programming
ResearchMethod
PrivacySecurity
EfficientAlgorithm
AdvancedAlgorithmicTech
AlgorithmGameTheory
LowCodeProject
ComputerCompose
Network
LinearMath
OperationSystem
Mathmatic
Fundamental Data Structures
Data structures make heavy use of pointers and dynamically allocated memory.
Stacks & Queues
ATD: Abstract Data Types
| ADT | data structures |
|---|---|
| list of supported operations | specify exactly |
| how data is represented | |
| what should happen | algorithms for operations |
| not: how to do it | has concrete costs |
| (space and running time) | |
| not: how to store data |
Stack
- Operators
- top(): Return the topmost item on the stack Does not modify the stack.
- push(x): Add 𝑥 onto the top of the stack.
- pop(): Remove the topmost item from the stack (and return it).
Queue
- Operators:
- enqueue(x): Add 𝑥 at the end of the queue.
- dequeue(): Remove item at the front of the queue and return it.
Resizable Arrays (可变大小的数组)
// Digression 题外话
- Array operations:
- create(n)
- get(i)
- set(i, x)
Arrays have fixed size (supplied at creation).
Doubling trick
maintain capacity 𝐶 = 𝑆.length so that 14 𝐶 ≤ 𝑛 ≤ 𝐶
-
How to maintain the last invariant?
-
before push: If 𝑛 = 𝐶, allocate new array of size 2𝑛, copy all elements.
-
after pop: If 𝑛 < 14 𝐶, allocate new array of size 2𝑛, copy all elements.
-
Amortized Analysis (摊销分析)
-
Any individual operation push / pop can be expensive! Θ(𝑛) time to copy all elements to new array.
-
But: An one expensive operation of cost 𝑇 means Ω(𝑇) next operations are cheap!
Formally: consider “credits/potential” Φ = min{𝑛 − 14 𝐶, 𝐶 − 𝑛} ∈ [0, 0.6𝑛]
amortized cost of an operation = actual cost (array accesses) − 4 · change in Φ
- cheap push/pop: actual cost 1 array access, consumes ≤ 1 credits ⇝ amortized cost ≤ 5
- copying push: actual cost 2𝑛 + 1 array accesses, creates 21 𝑛 + 1 credits ⇝ amortized cost ≤ 5
- copying pop: actual cost 2𝑛 + 1 array accesses, creates 12 𝑛 − 1 credits ⇝ amortized cost 5
- sequence of 𝑚 operations: total actual cost ≤ total amortized cost + final credits
- here: ≤ 5𝑚 + 4·0.6𝑛 = Θ(𝑚+𝑛)
Priority Queues & Binary Heaps
Priority Queue ADT
elements in the bag have different priorities.
-
Operators:
- construct(𝐴): Construct from from elements in array 𝐴.
- insert(𝑥,𝑝): Insert item 𝑥 with priority 𝑝 into PQ.
- max(): Return item with largest priority. (Does not modify the PQ.)
- delMax(): Remove the item with largest priority and return it.
- changeKey(𝑥,𝑝′): Update 𝑥’s priority to 𝑝′. Sometimes restricted to increasing priority.
-
PQ implementations
- Elementary implementations
- unordered list ⇝ Θ(1) insert, but Θ(𝑛) delMax
- sorted list ⇝ Θ(1) delMax, but Θ(𝑛) insert
- Elementary implementations
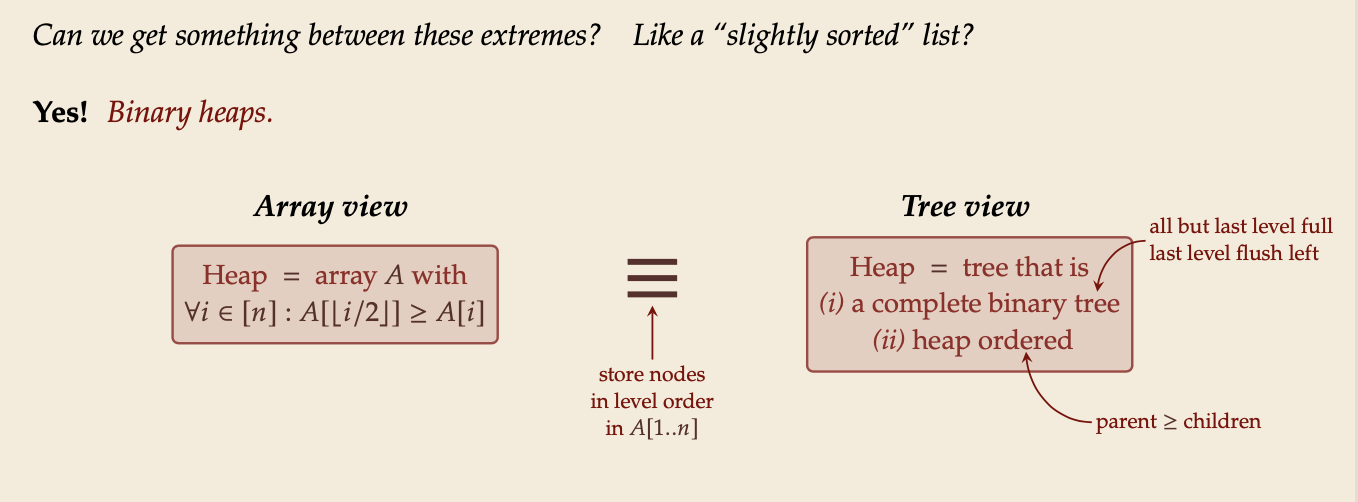
Why heap-shaped trees(堆形树)?
-
Why complete binary tree shape?
- only one possible tree shape
- complete binary trees have minimal height among all binary trees
- simple formulas for moving from a node to parent or children:
- parent at ⌊𝑘/2⌋
- left child at 2𝑘
- right child at 2𝑘+1
-
Why heap ordered?
- Maximum must be at root!
- But: Sorted only along paths of the tree; leaves lots of leeway for fast inserts
Operations on Binary Heaps
Insert
-
Add new element at only possible place: bottom-most level, next free spot.
-
Let element swim up(游上) to repair heap order.
Delete Max
- Remove max (must be in root).
- Move last element (bottom-most, rightmost) into root.
- Let root key sink in(沉入) heap to repair heap order.
Heap construction
-
𝑛 times insert ⇝ Θ(𝑛 log 𝑛)
-
instead:
- Start with singleton heaps (one element)
- Repeatedly merge two heaps of height 𝑘 with new element into heap of height 𝑘 + 1
-
Analysis
- Height of binary heaps:
- height of a tree: # edges on longest root-to-leaf path
- depth/level of a node: # edges from root ⇝ root has depth 0 𝑘
- How many nodes on first 𝑘 full levels?
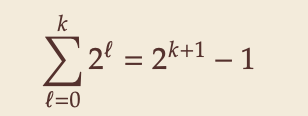
- Height of binary heaps:
Binary heap summary
| Operation | Running Time |
|---|---|
| construct(𝐴[1…𝑛]) | 𝑂(𝑛) |
| max() | 𝑂 (1) |
| insert(𝑥,𝑝) | 𝑂(log 𝑛) |
| delMax() | 𝑂(log 𝑛) |
| changeKey(𝑥,𝑝′) | 𝑂(log 𝑛) |
| isEmpty() | 𝑂 (1) |
| size() | 𝑂 (1) |