Formal
Algorithm
Common
Docker
Javascript
Network
Node
Notes
c++
c++Lib
golang
Javascript
Webpack
Vite
Webassembly
MCU
Protocol
ML
Compilation
DataStructure
Algorithm
MC_MP_Programming
ResearchMethod
PrivacySecurity
EfficientAlgorithm
AdvancedAlgorithmicTech
AlgorithmGameTheory
LowCodeProject
ComputerCompose
Network
LinearMath
OperationSystem
Mathmatic
Weighted Interval Scheduling 加权区间调度
Definition of Dynamic programming
-
A technique for solving optimisation problems.
-
The paradigm of dynamic programming:
-
Given a problem P, define a sequence of subproblems, with the following properties: (定义一系列的子问题)
-
The subproblems are ordered from the smallest to the largest. 从小问题到大问题
-
The largest problem is our original problem P. 最大的问题是 P
-
The optimal solution of a subproblem can be constructed from the optimal solutions of sub-sub-problems. (Optimal Substructure). 子问题的最优解可以被更小的子子问题最优解解决
-
-
Solve the subproblems from the smallest to the largest. When you solve a subproblem, store the solution (e.g., in an array) and use it to solve the larger subproblems.
Definition of Weighted Interval Scheduling
-
A set of requests {1, 2, … , n}.
-
Request i has a starting time s(i), a finishing time f(i), and a value v(i).
-
Alternative view: Every request is an interval [s(i), f(i)] associated with a value v(i).
-
-
Two requests i and j are compatible if their respective intervals do not overlap.
-
Goal: Output a schedule which maximises the total value of compatible intervals.
Subset Sum
The subset sum problem
-
We are given a set of n items {1, 2, … , n}.
-
Each item i has a non-negative weight wi.
-
We are given a bound W.
-
Goal: Select a subset S of the items such that sum_i wi <= W and sum_i 𝑤i is maximised.

Dynamic Programming
-
We need to identify the appropriate subproblems to use in order to solve the main problem.
-
Recall the weighted interval scheduling problem. Similar approach.
-
Let OPT(i) be the optimal solution to the subset sum problem, using a subset of {1, 2, … , i}.
- Let Oi be its value and hence O is On.
-
Should item n be in the optimal solution O or not?
-
If no, then OPT(n-1) = OPT(n)
-
If yes, ?
-
-
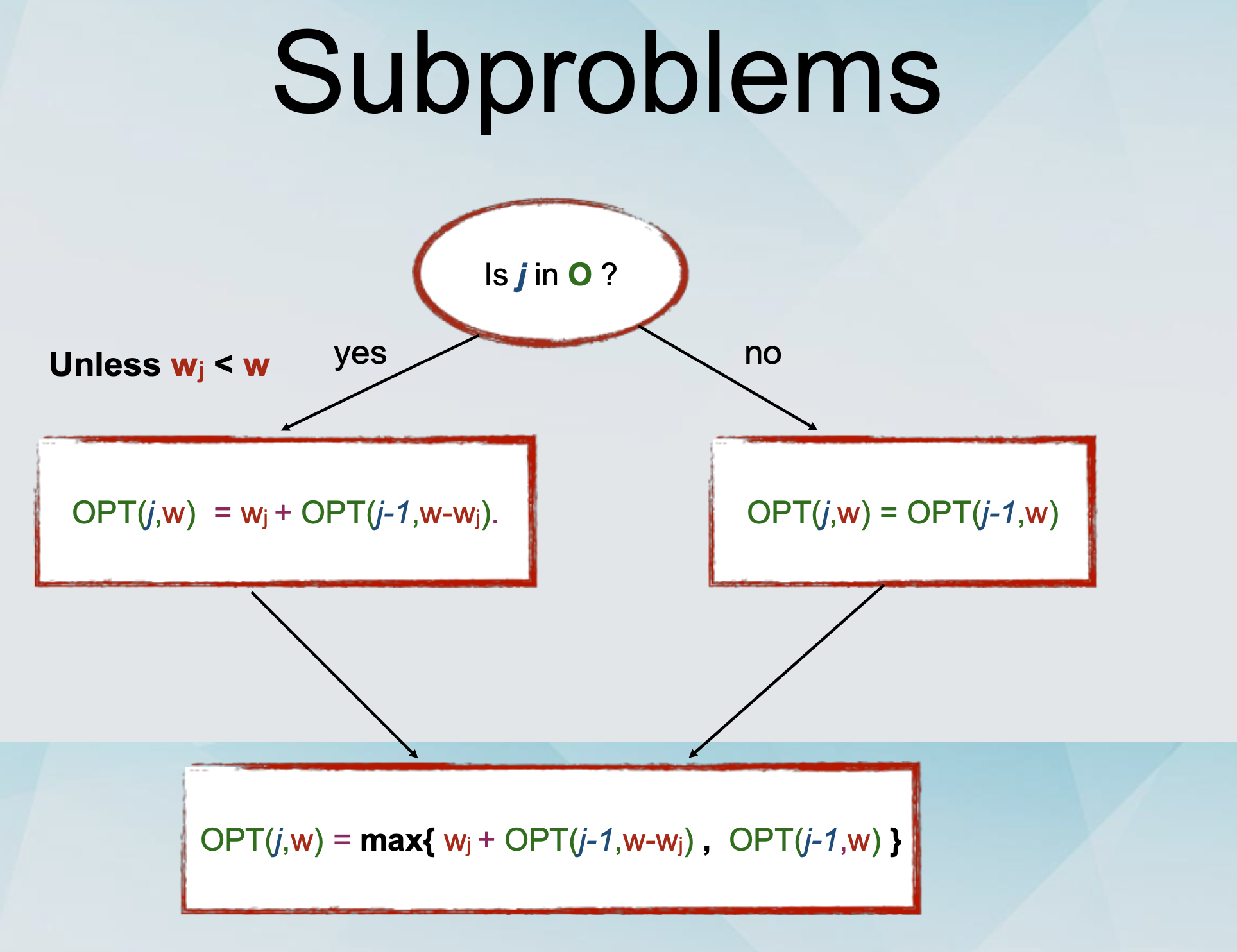
Subproblems
-
Using this notation, what are we looking for?
-
OPT(n,W)
-
Should item n be in the optimal solution O or not?
-
If no, then OPT(n,W) = OPT(n-1,W).
-
If yes, then OPT(n,W) = wn + OPT(n-1,W-wn).
-
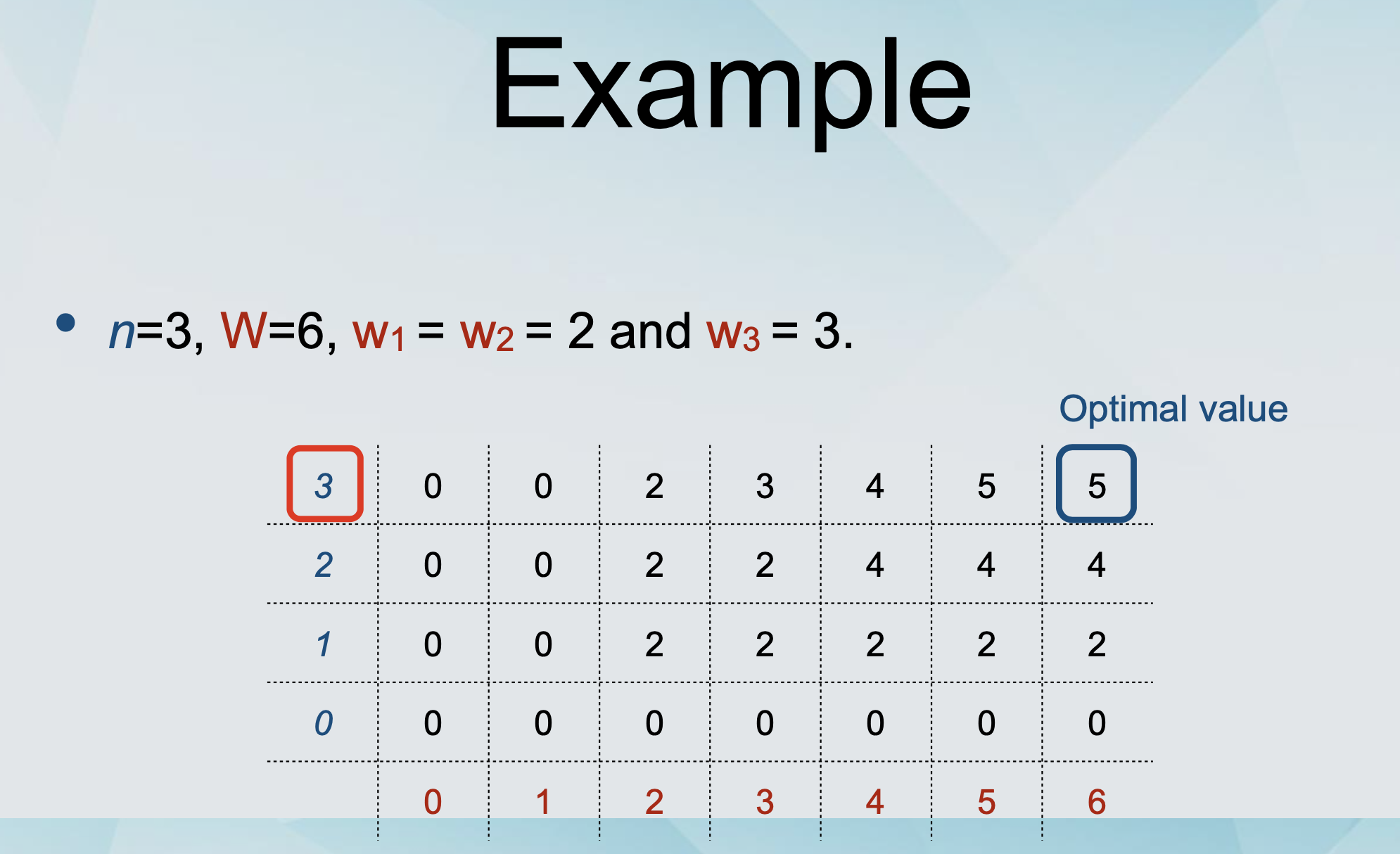
- Example
function subsetSum(arr, maxSum) {
let res = [[]];
for (let i = 0; i <= maxSum; i++) {
res[0].push(0);
}
for (let i = 1; i <= arr.length; i++) {
res[i] = [0];
for (let j = 0; j <= maxSum; j++) {
if (arr[i - 1] > j) {
res[i][j] = res[i - 1][j];
} else {
res[i][j] = Math.max(
res[i - 1][j],
arr[i - 1] + res[i - 1][j - arr[i - 1]]
);
}
}
}
console.log(res);
}
/**
*
*
3: [0, 0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5]
2: [0, 0, 2, 2, 4, 4, 4]
1: [0, 0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]
0: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
*/
- Running Time O(nW)
Knapsack
动态规划三大步骤
- 定义数组元素的含义,假设定义一个一维数组,那么需要明白 dp[i]代表什么意思
- 找出数组元素之间的关系式,类似于数学归纳法,当计算 dp[n]时,可以从 dp[n - 2],dp[n - 1]中推导出 dp[n]的值
- 找出初始值,例如 dp[4] = dp[3] + dp[2],而 dp[3] = dp[2] + dp[1]。dp[2]和 dp[1]不能再分,这就是初始值
案例
青蛙跳台阶(简单)
描述:一只青蛙一次可以跳上 1 级台阶,也可以跳上 2 级。求该青蛙跳上一个 n 级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
1.找出数组含义
dp[n]的含义是:青蛙跳上一个 n 级的台阶总共有多少种跳法
2.找出数组之间的关系式
由题可知,可以选择跳一级,也可以选择跳二级。所以可以得到 dp[n] = dp[n - 1] + dp[n - 2]
3.找出初始值
n 不能为负数,由题可知,dp[1] = 1,dp[0] = 0,dp[2] = 2。
写出算法
function getMethods(num) {
let dp = [0, 1, 2];
if (num <= dp.length) return dp[num]
for(let i = 3, i < num.length; i++) {
dp.push(dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2])
}
return dp[num.length - 1]
}
案例 2:找出到达终点的所有路径
描述:一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为 “Start” )。
机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为 “Finish” )。
问总共有多少条不同的路径?
dp 定义
表示有多少种方法可以走到 i,j 这个格子
找出数组之间的关系式
dp[i][j] = dp[m][n - 1] + dp[m - 1][n]
定义初始值
dp[0][0] = 1 dp[1][0] = 1 dp[0][1] = 1
写出算法
var dp = [[1, 1], [1]];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (!dp[i]) dp[i] = [];
if (!dp[i][j])
dp[i][j] = (dp[i][j - 1] || 0) + (i - 1 >= 0 ? dp[i - 1][j] : 0);
}
}
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];
案例 3: 最小路径和
给定一个包含非负整数的 m x n 网格 grid ,请找出一条从左上角到右下角的路径,使得路径上的数字总和为最小。 说明:每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。
dp 定义
dp[i][j] 表示路径数字总和的最小值
找出数组之间的关系式
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j]
找出默认值
dp[0][0] = grid[0][0]
题解
// dp[i][j] 表示路径数字总和的最小值
// dp[i][j] = min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j]
// 网格内有默认值
let m = grid.length;
let n = grid[0].length;
let dp = [[grid[0][0]]];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (!dp[i]) dp[i] = [];
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i === 0 && j === 0) continue;
if (j === 0) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + grid[i][j];
} else if (i === 0) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] + grid[i][j];
} else {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]) + grid[i][j];
}
}
}
return dp[m - 1][n - 1];