Algorithm
Common
Docker
Javascript
Network
Node
JavaScript与网络基础
日期:2022-09-16 18:23:14
更新:2022-09-16 18:25:23
标签:面试, JavaScript, 计算机网络
分类:面试, JavaScript
本文是作者在复习前端知识时总结的JavaScript基础,数据结构和算法,计算机网络的知识点。给大家一起学习交流。

前言
本文是作者在复习前端知识时总结的 JavaScript 基础,数据结构和算法,计算机网络的知识点。给大家一起学习交流。
考虑到篇幅问题,作者把前端知识分开多个文章不同知识点地去讲述,本文是前端基础系列的第一篇文章。
文章可能会有一些未涉及的知识点,作者也会持续更新下去。
作者知识水平有限,如有错误纰漏,望大家指正。
Javascript 基础
1.数据类型
Javascript 数据类型由基础值和对象组成
- 基础值
Boolean布尔值
Null空值
Undefined未定义
Numeric数字类型,由Number和BigInt组成
String字符串
Symbol一个唯一的不可变的原始值 - 对象
对象是内存中可能被标识符引用的值。
对象分为两种属性:数据属性和存取器属性
2.作用域
作用域是指当前的执行上下文,其中值和表达式是可见的或可引用的。如果指或表达式不在当前作用域,它将不会允许被使用。作用域是一种层次结构,所以子作用域允许访问父作用域,反之则不行
JavaScript 中有以下几种作用域:
- 全局作用域:给所有代码运行时默认作用域
- 模块作用域:在模块中运行代码的作用域
- 函数作用域:函数创建时的作用域
"use strict"; function test() { const t1 = "test"; console.log(t1); // test } test(); console.log(t1); // error - 块级作用域:使用
let和const声明值时创建的作用域"use strict"; { var a = "a"; let b = "b"; } console.log(a); // a console.log(b); // error
3.变量提升(Hoisting)
-
变量提升指的是:JS 的解析器会在代码执行前将函数,变量或类移动到作用域的最顶端声明。
function t() { console.log(t1); // undefined var t1 = "t1"; } // 变量提升后 function t() { var t1; console.log(t1); t1 = "t1"; } -
变量提升允许函数在声明之前安全地使用
t(); // aa function t() { return "aa"; } -
let和const的变量提升let 和 const 与 var 不一样,它们不会初始化默认值。当我们在声明之前使用 let 或 const 生命的变量,则会报变量未初始化的错
function t() { console.log(t1); // error uninitialized let t1 = "aa"; }
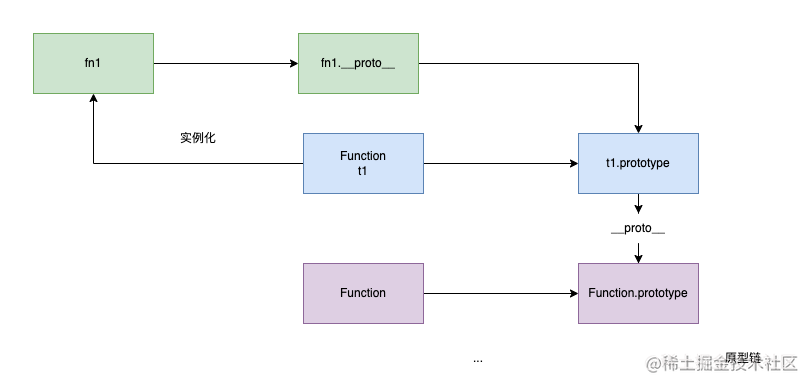
4. 原型与原型链
原型:JavsScript 中每个对象都有一个__proto__属性,这个属性的值是一个普通对象,并且指向该对象的构造函数的prototype。
原型链:当我们试图获得对象里面的某个属性时,如果对象中没有,则他会隐式地在__proto__中查找。
5. 继承
-
原型链继承:实现简单,缺点:多个实例对引用类型的操作会被篡改。
function SuperType() { this.super = true; } SuperType.prototype.getSuper = function () { return this.super; }; function SubType() { this.sub = false; } // subType的原型指向父类的实例 SubType.prototype = new SuperType(); SubType.prototype.getSub = function () { return this.sub; }; console.log(new SubType());Copy to clipboardErrorCopied -
借用构造函数继承:
缺点:- 只能继承父类的实例属性和方法,不能继承原型属性和方法
- 无法实现复用,每个子类都有父类实例函数的副本,影响性能
function SuperType() { this.test = false; } function SubType() { SuperType.call(this); } console.log(new SubType());Copy to clipboardErrorCopied -
组合继承: 用原型链实现对原型属性和方法的继承,用借用构造函数技术来实现实例属性的继承。
缺点:- 子类创建实例时,原型中会存在两份相同的属性/方法
function SuperType() { this.test = false; } SuperType.prototype.getTest = function () { return this.test; }; function SubType() { // 第二次调用 SuperType.call(this); this.sub = 123; } // 第一次调用 SubType.prototype = new SuperType(); // 修改SubType的构造器,使其指向SubType SubType.prototype.constructor = SubType; SubType.prototype.getSub = function () { return this.sub; }; console.log(new SubType());Copy to clipboardErrorCopied -
原型式继承:利用一个空对象作为中介,将某个对象直接赋值给空对象构造函数的原型。(Object.create)
缺点:- 原型链继承多个实例的引用属性指向相同,存在篡改可能
- 无法传递参数
function Extend(obj) { function F() {} F.prototype = obj; return new F(); }Copy to clipboardErrorCopied -
寄生继承: 在原型式继承的基础上,增强对象,返回构造函数
缺点:- 原型链继承多个实例的引用属性指向相同,存在篡改可能
- 无法传递参数
function obj(obj) { function F() {} F.prototype = obj; return new F(); } function Extend(origin) { // 函数的主要作用是为构造函数新增属性和方法,以增强函数 let clone = obj(origin); clone.getTest = function () { return test; }; return clone; }Copy to clipboardErrorCopied -
寄生组合继承: 结合借用构造函数传递参数和寄生模式实现继承
function extend(subType, superType) { // 原型式继承 let prototype = Object.create(superType.prototype); prototype.constructor = subType; // 增强对象,弥补因重写原型而失去的默认的constructor 属性 subType.prototype = prototype; // 指定对象,将新创建的对象赋值给子类的原型 } // test // 父类初始化实例属性和原型属性 function SuperType(name) { this.name = name; this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"]; } SuperType.prototype.sayName = function () { alert(this.name); }; // 借用构造函数传递增强子类实例属性(支持传参和避免篡改) function SubType(name, age) { SuperType.call(this, name); this.age = age; } extend(SubType, SuperType); const test = new SubType(); console.log(test);
6. 闭包
定义:在函数内声明一个内层函数,内层函数又改变外层函数变量的值
作用:
- 能够访问函数定义时所在的词法作用域
- 私有化变量
- 模拟块级作用域
- 创建模块
缺点: 会使变量持续存在一个内存中,不被回收
function closure() {
var x = 1;
return (function () {
return x;
})();
}
closure(); // 1
7.EventLoop
JS 是单线程的,为了防止一个函数执行时间过长阻塞后面的代码,所以会先将同步代码压入执行栈中,依次执行,将异步代码推入异步队列,异步队列又分为宏任务队列和微任务队列。
- 宏任务 (setInterval,setTimeout,setImmediate)
- 微任务 (Promise.then,async/await,MutationObserver)
(function () {
console.log("111");
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log("222");
resolve();
}).then(() => {
console.log("333");
});
setTimeout(() => {
console.log("444");
}, 0);
console.log("555");
})();
// 111
// 222
// 555
// 333
// 444
8. 栈(stack)与堆(heap)与垃圾回收
-
栈:特性是后进先出,用于存储 javascript 中的基本类型和引用类型的指针,每个 V8 进程都会有一个栈区域,它的存储顺序是连续的,所以在新增或删除数据是也只需要将指针移动到对应的位置,然后删除或修改数据,所以栈的速度非常快。
-
堆:是 V8 内存分配一个重要的组成部分,主要用于存储 js 中的
引用类型。
JavaScript 的垃圾回收是由 JS 引擎自动执行的,内存的分配空间使用分为新生代和老生代
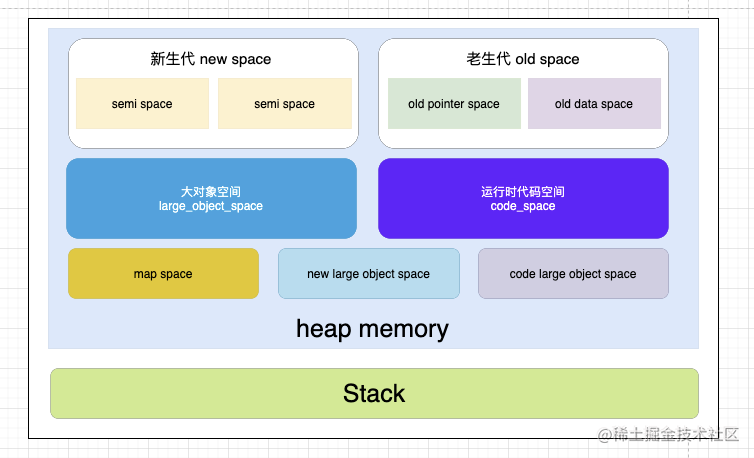
新生代内存是最有可能被回收的老生代内存,可以理解为多次被使用,常驻于内存空间中的内存。这些内存回收检测的周期相对比较慢
常用的垃圾回收方法:标记清除法和引用计数法
9.浏览器缓存
- Cookie
- Cookie 是以 Key-Value 形式的一小段的文本信息,大小大约只有 4KB。
- Cookie 是服务器向客户端返回的,浏览器接收到后会把 Cookie 保存起来。
- 当浏览器再次请求该域名时,会把 Cookie 也带上交给服务器。
- 服务器检测到 cookie 后,来确认用户信息
- sessionStorage & localStorage
- HTML5 中新增的浏览器缓存,以字符串的形式保存数据,相比 Cookie 有更大的空间,有大约 5MB。
- sessionStorage 在当用户关掉浏览器窗口后就会清除
- localStorage 则会一直保存除非手动清除,不然不会清除。
- indexDB
- IndexedDB 是一种底层 API,用于在客户端存储大量的结构化数据
TypeScript
1.TypeScript 修饰符
- public 可以在任何地方访问
- protected 可以在子类中访问
- private 不能被继承,只能在内部访问
- readonly 只读
2. 普通枚举和 const 枚举的区别
- 普通枚举会被编译成一个对象
- const 内举在编译时则会被删除掉,避免额外的性能开销
// 普通枚举
enum Test {
T1 = "T1",
}
console.log(Test.T1);
// const 枚举
const enum Test1 {
T1 = "T1",
}
console.log(Test1.T1);
编译后
// 普通枚举编译后
var Test;
(function (Test) {
Test["T1"] = "T1";
})(Test || (Test = {}));
console.log(Test.T1);
// const枚举
console.log("T1" /* Test1.T1 */);
3. type 和 interface 的区别
- type 可以为任何类型引入名称
- type 不支持继承,但可以使用 & 将两个 type 组合成一起
type t1 = {
a: string;
};
// t2 = { a: string, b: string }
type t2 = {
b: string;
} & t1;
- type 不会创建一个真正的名字
- type 无法被 implement
- type 重名时会抛出错误,interface 重名则会合并
4.复杂类型推导
见链接
5.TypeScript 中的工具类型有哪些
- Partial<Type> 返回一个指定类型的子集
- Required<Type> 指定类型的所有属性变为必须实现
- Readonly<Type> 置顶类型变为只读
- Record<keys, Type> 生成一个值类型为 Type 的对象类型
- Pick<Type, keys> 在指定类型中指定 key,并返回一个新对象
- Omit<Type, keys> 在制定类型中删除置顶的 key,并返回一个新对象
- Exclude<UnionType, ExcludeMembers> 在一个联合类型中提出成员变量
- Extract<UnionType, Union> 在一个联合类型中返回指定 key 的联合类型
- NonNullable<Type> 剔除 null 或 undefined 类型
- Parameters<Type> 返回函数中的参数的类型
- ConstructorParameters<Type> 返回类构造函数中的类型
- ReturnType<Type> 返回一个函数的返回类型
- InstanceType<Type> 返回一个类构造函数的返回值类型
- ThisParameterType<Type> 返回函数参数重 This 参数的类型
- OmitThisParameter<Type> 去掉函数参数重的 this 参数,返回去掉 this 参数后的函数类型
- ThisType<Type> 这个工具函数不会返回类型,它用作上下文类型标记。函数没有返回值时才可以使用该工具
6.unknow与any的区别
unknow 类型赋值给其他类型前,必须被断言
7. 什么是泛型
泛型可以用来创建可重用的组件,一个组件可以支持多种类型的数据。 这样用户就可以以自己的数据类型来使用组件
JavaScript 工作原理
JavaScript 是一门解析型语言,没有编译的步骤,它是“边解析边执行”的。
通常解析型语言执行如下:
- 用解析器将源代码生成 AST 树(抽象语法树)
- 解析抽象语法树解析成机器码并立即执行
虽然解析性语言无需编译,只需要提供一个解析器就能执行代码。 但是相对的,每次执行都需要将源代码解析一遍,执行效率很低。
因此,JS 的执行引擎中会进行很多优化,让我们的 JS 代码执行得更快。
以 google 的 V8 引擎为例,V8 的执行 JS 的过程如下:
- 源代码到 AST:用解析器将源代码生成 AST 树(抽象语法树)
- AST 到字节码:将抽象语法书解析成字节码
- 字节码到机器码:V8 的
TurboFan会将字节码生成一个图表,用高性能的机器码去替换部分字节码
Just-In-Time(JIT)
上面说到了:解析型语言的缺点就是效率很低,每次执行都要解析一遍。为此 V8 引擎加入了即时编译。
基本思想是:避免代码的重复转换。开始时,解析器会通过编译简单地运行代码,在执行代码期间,解析器会跟踪代码片段,运行几次后会记录下运行几遍的热代码和运行多遍的代码。JIT 会将热代码片段转到基线编译器(baseline compiler),尽可能地重用这些编译后的代码。
How JavaScript works: Optimizing the V8 compiler for efficiency
手写代码
1. bind,call,apply
// Call
Function.prototype.MyCall = function (scope, ...args) {
const ctx = scope ? Object(scope) : window;
ctx.fn = this;
const res = args.length ? ctx.fn(...args) : ctx.fn();
return res;
};
// Apply
Function.prototype.MyApply = function (scope, args) {
if (!Array.isArray(args)) {
throw new Error("args is not a array");
}
const ctx = scope ? Object(scope) : window;
ctx.fn = this;
const res = args.length ? ctx.fn(...args) : ctx.fn();
return res;
};
// Bind
Function.prototype.MyBind = function (scope, args) {
if (!Array.isArray(args)) {
throw new Error("args is not a array");
}
return () => {
this.call(scope, ...args);
};
};
// test
var obj1 = {
test: "t1",
};
var obj2 = {
test: "t2",
getInfo(num) {
console.log(num, this.test);
},
};
obj2.getInfo.MyCall(obj1, 100); // 100, t1
obj2.getInfo.MyApply(obj1, [100]); // 100, t1
obj2.getInfo.MyBind(obj1, [100])(); // 100, t1
2. 防抖和节流
// 防抖 函数在n时秒后执行,执行前重新调用则会重新计时
function debounceFunc(func, during) {
let timer = null;
return function (...args) {
if (timer) clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(() => {
func(...args);
}, during);
};
}
// 节流 n秒内只触发一次
function throttledFunc(func, during) {
let timer = null;
return function (...args) {
if (timer) return;
timer = setTimeout(() => {
func(...args);
clearTimeout(timer);
}, during);
};
}
// test
var deb = debounceFunc((num) => {
console.log(`${num} debounce func execute`);
}, 300);
var thr = throttledFunc((num) => {
console.log(`${num} throttled func execute`);
}, 300);
for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
deb(i); // 999 debounce func execute
thr(i); // 0 throttled func execute
}
3. new
function MyNew(obj, ...args) {
// 1. 声明一个对象
// 2. 该对象的原型指向 func的原型
// 3. 调用该函数,如果调用后返回一个对象,则return它,如果没有,则rteurn声明的对象
let newObj = {};
newObj.__proto__ = obj.prototype;
let res = obj.call(newObj, ...args);
if (res !== null && (typeof res === "object" || typeof res === "function")) {
return res;
}
return newObj;
}
// test
function Test(aa, bb) {
this.t1 = aa;
this.t2 = bb;
}
var res = MyNew(Test, "test1", "test2");
console.log(res.t1); // test1
console.log(res.t2); // test2
4. 手写 Promise
function MyPromise(func) {
if (typeof func !== "function") {
throw new Error("func is not a function");
}
this.pedding = 0;
this.resolve = 0;
this.reject = 0;
this.thenFun = [];
this.errFun;
this.finallyFun;
this.val;
this.__init__(func);
}
MyPromise.prototype.__init__ = function (func) {
if (this.pedding) return;
this.pedding = 1;
func(this.__resolve__.bind(this), this.__reject__.bind(this));
};
MyPromise.prototype.__resolve__ = function (data) {
if (!this.pedding) return;
this.resolve = 1;
this.val = data;
this.__callFunc__();
};
MyPromise.prototype.__reject__ = function (data) {
if (!this.pedding) return;
this.reject = 1;
this.val = data;
this.__callFunc__();
};
MyPromise.prototype.__callFunc__ = function () {
if (this.pedding && this.resolve) {
const fn = this.thenFun.shift();
if (!fn) {
this.finallyFun && this.finallyFun();
return;
}
if (this.val instanceof MyPromise) {
const cur = this;
this.val.then((msg) => {
this.val = fn(msg) || undefined;
this.__callFunc__();
});
} else {
this.val = fn(this.val) || undefined;
this.__callFunc__();
}
} else if (this.pedding && this.reject && this.errFun) {
this.errFun(this.val);
this.finallyFun && this.finallyFun();
}
};
MyPromise.prototype.then = function (fn) {
if (typeof fn !== "function") {
throw new Error("fn is not a function");
}
if (this.pedding) {
if (!this.resolve) this.thenFun.push(fn);
else fn(this.val);
}
return this;
};
MyPromise.prototype.catch = function (fn) {
if (typeof fn !== "function") {
throw new Error("fn is not a function");
}
if (this.pedding) this.errFun = fn;
};
MyPromise.prototype.finally = function (fn) {
if (typeof fn !== "function") {
throw new Error("fn is not a function");
}
if (this.pedding) this.finallyFun = fn;
};
// test
new MyPromise((res, rej) => {
setTimeout(() => {
res(111);
}, 3000);
})
.then((msg) => {
console.log(msg);
return 222;
})
.then((msg) => {
console.log(msg);
return new MyPromise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(333);
}, 3000);
});
})
.then(console.log)
.finally(() => {
console.log("finally");
});
// 111
// 222
// 333
// finally
5.深拷贝
function checkType(obj, typeName) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) === `[object ${typeName}]`;
}
function deepCloneObj(obj) {
let res;
if (checkType(obj, "Object")) {
res = {};
for (let x in obj) {
res[x] = typeof obj[x] === "object" ? deepCloneObj(obj[x]) : obj[x];
}
} else if (checkType(obj, "Array")) {
res = [];
for (let x of obj) {
res.push(typeof x === "object" ? deepCloneObj(x) : x);
}
} else {
res = obj;
}
return res;
}
// test
var test = {
a: "aa",
b: { c: "cc" },
c: ["a", { b: "bb" }],
};
deepCloneObj(test);
6. 手写 instanceOf
function MyInstanceOf(obj, target) {
let proto = obj.__proto__;
while (proto) {
if (proto === target.prototype) {
return true;
}
proto = proto.__proto__;
}
return false;
}
7. 函数柯里化
// 定长柯里化
function MyCurryFun(fn, ...args) {
const fnParamLen = fn.length;
return function (...currentArgs) {
const postData = [].concat(args, currentArgs);
if (postData.length >= fnParamLen) {
return fn.call(null, ...postData);
} else {
return MyCurryFun.call(null, fn, ...postData);
}
};
}
// 不定长柯里化
function MyCurry(fn, ...args) {
function curried(...currentArgs) {
const postData = [...args, ...currentArgs];
return MyCurry.call(null, fn, ...postData);
}
curried.toString = function () {
return fn.apply(null, args);
};
return curried;
}
// test
var fn1 = MyCurryFun((a, b, c) => a * b * c);
console.log(fn(1)(2)(3)); // 6
var fn2 = MyCurry((...args) => args.reduce((a, b) => a + b));
// 由于浏览器实现问题,console.log 不会打印返回值
alert(fn(1, 2)(3)); // 6
8. 寄生组合继承
function extends(parent, child) {
const obj = Object.create(child.prototype)
obj.constructor = parent
child.prototype = obj
}
// 父类初始化实例属性和原型属性
function SuperType(name) {
this.name = name;
this.colors = ['red', 'blue', 'green'];
}
SuperType.prototype.sayName = function () {
alert(this.name);
};
// 借用构造函数传递增强子类实例属性(支持传参和避免篡改)
function SubType(name, age) {
SuperType.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
extend(SubType, SuperType);
const test = new SubType();
console.log(test);
数据结构和算法
数据结构
1.栈
栈(stack)是限定仅在表尾(栈顶)进行插入或删除操作的线性表。进出栈的原则为:后进先出
栈的实现
class MyStack {
constructor() {
this.data = [];
}
push(val) {
this.data.push(val);
return true;
}
pop() {
return this.data.pop();
}
len() {
return this.data.length;
}
}
2.队列
队列(queue)是一种遵循先进先出的线性表。
队列的实现
class MyQueue {
constructor() {
this.data = [];
}
push(val) {
this.data.push(val);
return true;
}
pop() {
return this.data.shift();
}
len() {
return this.data.length;
}
}
3. 链表
用一组任意的存储单元存储的数据元素,每个元素都由两部分组成:数据域和指针域。
数据域负责存放数据,指针域负责保存数据在内存中的位置。
我们把这些数据元素的指针域连在一起组成的一条链式结构,称为链表
// 单链表
class SingleLink {
constructor() {
this.obj = {
value: null,
next: null,
};
this.last = this.obj; // 尾指针
this.count = 0;
}
// 插入链表
add(val) {
let pushData = {
value: val,
next: null,
};
this.last.next = pushData;
this.last = pushData;
this.count++;
return true;
}
// 指定位置插入
insert(val, position) {
if (!position) {
throw new Error("position is undefined");
}
if (position > this.count - 1) {
throw new Error("position is too large than link total num");
}
let pushData = {
value: val,
next: null,
};
let cur = 0;
let tmp = this.obj.next;
// 查找插入位置的前一个节点
while (cur < position - 1) {
tmp = tmp.next;
cur++;
}
let next = tmp.next;
tmp.next = pushData;
pushData.next = next;
if (position === this.count - 1) {
this.last = pushData;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
// 删除链表
delete(num) {
if (num > this.count) {
throw new Error("num is larger than link total num");
}
let tmp = this.obj.next;
let cur = 0;
while (cur < num - 1 && tmp.next) {
tmp = tmp.next;
cur++;
}
tmp.next = tmp.next.next;
if (num === this.count - 1) {
this.last = tmp;
}
this.count--;
return true;
}
len() {
return this.count;
}
}
4.二叉树
class BTree {
constructor() {
// 二叉树结构
this.tree = {
val: null,
left: null,
right: null,
};
}
// 前序遍历 先根 再左 最后右
front(cur, arr = []) {
if (cur.val !== null) {
arr.push(cur.val);
}
if (cur.left) {
this.front(cur.left, arr);
}
if (cur.right) {
this.front(cur.right, arr);
}
return arr;
}
// 中序遍历 先左 后中 最后右
middle(cur, arr = []) {
if (cur.left) {
this.middle(cur.left, arr);
}
if (cur.val !== null) {
arr.push(cur.val);
}
if (cur.right) {
this.middle(cur.right, arr);
}
}
// 后序遍历 先左 再右 最后中
after(cur, arr = []) {
if (cur.left) {
this.after(cur.left, arr);
}
if (cur.right) {
this.after(cur.right, arr);
}
if (cur.val !== null) {
arr.push(cur.val);
}
}
}
5.图
图是一种比二叉树要复杂的数据结构,由边和顶点组成,遍历图的方式有两种:深度优先(DFS)和广度优先(BFS)
let data = {
val: "A",
children: [
{
val: "B",
children: [
{
val: "C",
children: [
{
val: "D",
},
],
},
{
val: "E",
},
],
},
{
val: "F",
},
],
};
// 深度优先
function dfs(root, stack = [], target) {
stack.push(root.val);
if (root.children && root.children.length) {
root.forEach((val) => {
dfs(val, stack, target);
});
stack.pop();
} else {
const cur = stack.pop();
if (cur === target) {
console.log(`${stack.join(" => ")} => ${target}`);
return;
}
}
}
dfs(data, [], "E"); // A => B => E
// 广度优先
function bfs(root, queue = [], target) {
queue.push(root);
while (queue.length) {
const tmp = queue.shift(); // 队首出列
if (target === tmp.val) {
if (tmp.pre && tmp.pre.length) {
console.log(`${tmp.pre.join(" => ")} => ${target}`);
}
return;
}
if (tmp.children && tmp.children.length) {
tmp.children.forEach((val) => {
const pre = tmp.pre ? [...tmp.pre, tmp.val] : [tmp.val];
val.pre = pre; // 记录遍历路径
queue.push(val);
});
}
}
}
bfs(data, [], "E"); // A => B => E
基本算法
1.冒泡排序
时间复杂度 O(n2)
```javascript
function sort(arr) {
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for(let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
if(arr[i] > arr[j]) {
let tmp = arr[i]
arr[i] = arr[j]
arr[j] = tmp
}
}
}
return arr;
}
// test
var t = [3,1,4,2]
console.log(sort(t)) // [1,2,3,4]
```
2.选择排序
选择排序由两个循环组成:
-
外层循环负责排列数据,内层循环负责比较元素,内层每次循环都会得出一个最小的索引值。
-
得出最小值后将外层的当前元素与最小的元素替换
-
时间复杂度 O(n2)
// 简单选择排序 function simplySelectionSort(arr) { for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { let minIndex = i; for (let j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) { if (arr[minIndex] > arr[j]) { minIndex = j; } } let tmp = arr[minIndex]; arr[minIndex] = arr[i]; arr[i] = tmp; } return arr; } var arr = [2, 3, 1, 45, 7]; console.log(simplySelectionSort(arr)); // [1,2,3,7,45]
3.插入排序
插入排序基本原理:将一个记录插入到已经排好序的有序表中,从而一个新的、记录数增 1 的有序表。在其实现过程使用 双层循环,外层循环对除了第一个元素之外的所有元素,内层循环对当前元素前面有序表进行待插入位置查找,并进行移动。
时间复杂度 O(n2)
// 插入排序
function insertSort(arr) {
let res = [arr[0]];
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
let isInsert = false;
for (let j = 0; j < res.length; j++) {
if (res[j] > arr[i]) {
j === 0 ? res.unshift(arr[i]) : res.splice(j, 0, arr[i]);
isInsert = true;
break;
}
}
if (!isInsert) {
res.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return res;
}
// test
var arr = [22, 2, 1, 5, 3, 7, 1];
insertSort(arr); // [1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 22]
4.快速排序
快速排序基本思想:找出一个基准项,将数组分为两部分,一部分是小于基准项的,另一部分是大于中间项的。然后再分别将这两个基准项进行快速排序,把序列变为有序的。
快速排序是不稳定的。
时间复杂度:O(n * log n)
```javascript
// 快速排序
function quickSort(arr) {
const flag = arr[0]; // arr[0] 为基准项
let left = [];
let right = [];
for(let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > flag) {
right.push(arr[i])
} else {
left.push(arr[i])
}
}
if (left.length > 1) {
left = quickSort(left)
}
if (right.length > 1) {
right = quickSort(right)
}
return [].concat(left, [flag], right)
}
// test
var arr = [7,6,9,3,1,5,2,4,5,6,7,1,2,3,5,6,8,1,2,3,6,8,0,1,2,3,6];
quickSort(arr); // [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9]
```
5.希尔排序
希尔排序是插入排序的一种改进版本,但是希尔排序并不稳定。
希尔排序的基本思想:通过比较相距一定间隔(增量)的元素,每次比较所用的距离随着算法的进行而缩小,直到比较到相邻元素为止。
那么如何确定间隔增量,是我们在实现算法过程中序啊哟考虑的事情。
时间复杂度:O(n(1.3—2))
```javascript
// 希尔排序
function shellSort(arr) {
let num = Math.ceil(arr.length / 2)
while(num > 0) {
for(let i = num;i < arr.length; i++) {
let x = i;
let tmp = arr[x];
while(x - num >= 0 && tmp < arr[x - num]) {
arr[x] = arr[x - num]
x -= num
}
arr[x] = tmp
}
num = num === 1 ? 0 : Math.ceil(num / 2)
}
return arr
}
// test
var arr = [7,6,9,3,1,5,2,4,5,6,7,1,2,3,5,6,8,1,2,3,6,8,0,1,2,3,6];
shellSort(arr); // [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9]
```
6.归并排序
归并排序是非常典型的分治算法,基本思想是:将序列一分为二,两个序列分别再分为两个序列,直到最后的一个序列的长度为 1,然后再将它们排列后合并,合并的方法采用双指针的方式比较两个序列。
时间复杂度:O(n * log n)
归并排序是稳定的排序
```javascript
// 归并排序
function mergeSort(arr) {
// 分
const middle = Math.floor(arr.length / 2);
let left = arr.slice(0, middle);
let right = arr.slice(middle, arr.length);
if (left.length > 1) {
left = mergeSort(left);
}
if (right.length > 1) {
right = mergeSort(right);
}
// 并
let res = [];
while(left.length && right.length) {
if (left[0] > right[0]) {
res.push(right.shift());
} else {
res.push(left.shift());
}
}
if (left.length) {
res = res.concat(left)
} else {
res = res.concat(right)
}
return res;
}
// test
var arr = [7,6,9,3,1,5,2,4,5,6,7,1,2,3,5,6,8,1,2,3,6,8,0,1,2,3,6];
mergeSort(arr); // [0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9]
```
7.二分查找
二分查找是一种在序列中查找数据的算法,它只能查找已经排序好的数据。
将序列分开为两部分,判断目标值与分开序列的基准值比较,如果等于,直接返回。
如果大于基准值,则目标值可能在基准值的右边,反之亦然(也有可能目标值不存在序列中)。
再利用递归查询目标值可能在的数组。
// 二分查找
function sliceSort(arr, target) {
if (arr.length === 1 && arr[0] !== target) return false;
const base = Math.floor(arr.length / 2);
if (arr[base] === target) {
return true;
} else {
if (arr[base] > target) {
return sliceSort(arr.slice(0, base), target);
} else {
return sliceSort(arr.slice(base + 1, arr.length), target);
}
}
}
// test
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7];
sliceSort(arr, 6); // true
sliceSort(arr, 9); // false
计算机网络
TCP/IP
TCP/IP 是一个协议集合,它简化了 OSI 协议标准,分为四层。
分别是:
应用层:HTTP,DNS,FTP,SMTP,POP3 等协议传输层:负责转发数据,分为可靠传输和不可靠传输。主要协议:TCP,UDP网际层(网络互联层):负责分配网络中的唯一地址,转发和路由选择。主要协议:IP网络接口层:负责处理传输介质相关的细节,主要协议 PPP(点到点协议),以太网,令牌环,ATM,帧中继等。
我们现在的 Internet 就是基于 TCP/IP 而建立的。
HTTP
HTTP(超文本传输协议)是应用层协议,基于 TCP,主要用于Web的数据传输。
HTTP 主要的工作流程为:
- 1.Web 端向服务器发起获取资源的请求
- 2.Web 与服务器端建立 TCP 链接
- 3.传输数据
HTTP 数据传输方式
- 流水:在一个 HTTP 请求完成后才能进行下一个 HTTP 请求
- 非流水:一次发送多个 HTTP 请求,当一个数据发送完成后再向服务器端响应
目前 HTTP 版本主要有:
- 1.0:早期主要使用的 HTTP 协议,不支持持久链接,每请求一个数据都需要建立一次 TCP,获取完数据再拆除,所以效率很低。
- 1.1:是 HTTP1.1 的改进版,改进了,支持持久的 HTTP,在获取多个资源时只需要建立一个 TCP 链接,通过该 TCP 链接获取资源。
- 2.0:是新一代的 HTTP 版本,支持多路复用,使用二进制传输流,针对头部进行了头部压缩,还有服务端主动推送的功能。了解更多
HTTP 报文:
-
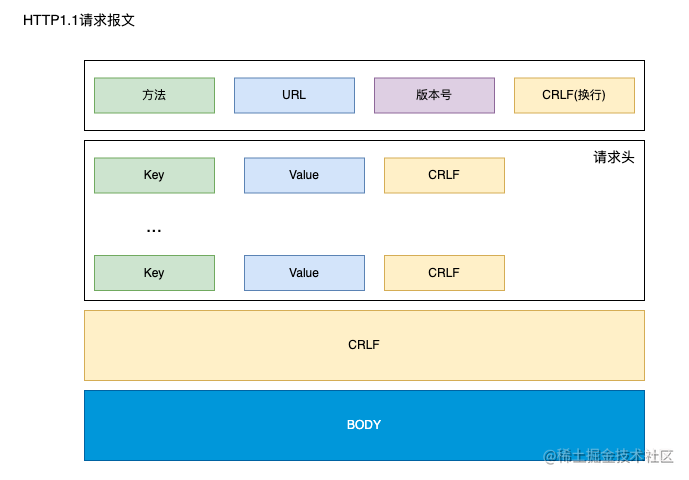
-
响应报文
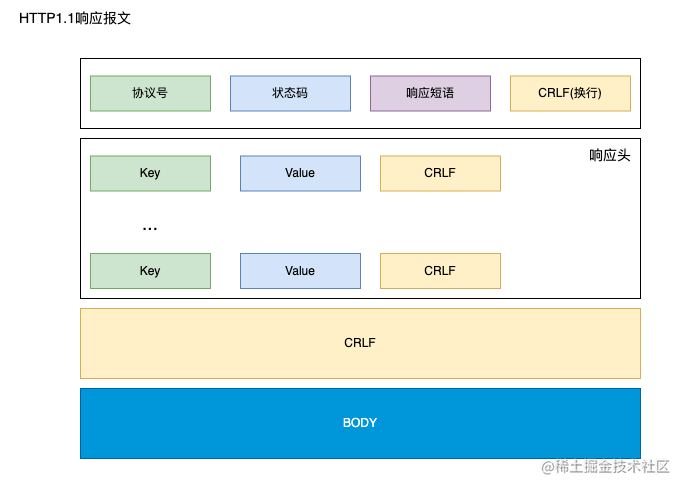
HTTP 缓存
-
强缓存:在向服务器请求之前,会先向浏览器缓存查找,是否有这个缓存,查找缓存的根据是
url。 如果有缓存则立即返回数据。强缓存是会保存到硬盘或者内存中的- 设置强缓存:通过 Headers 的 Expires 或 Cache-Control 设置
- 设置优先级:Cache-Control > Expires
-
协商缓存:当强缓存失效后,浏览器会携带缓存标识去请求资源,服务器根据缓存标识来决定是否使用缓存。
- 设置协商缓存:通过 Headers 的 Last-Modified 或 Etag 设置
- 判断协商缓存:判断 Headers 是否存在 If-Modified-Since 或 If-None-Match
- 强缓存优先级高于协商缓存
DNS
DNS(域名系统)主要用于查找域名对应的 IP 地址的应用层协议,它是基于 UDP 协议的。
- DNS 查找是一个 C-S(client-server)的结构,通过向域名服务器查找域名对应的 IP。
- 域名服务器是一个
层级结构,主要分为四层,分别是:根域名服务器,权威域名服务器,顶级域名服务器和本地域名服务器。 - DNS 查询的方式有两种,分别是:
递归查询和迭代查询。 - 点击这里,了解更多。
FTP
FTP(文件传输协议)主要用于主机之间的文件传输,它是一个基于 TCP 的应用层协议。
FTP 主要分为两个链接:
- 控制链接:主要负责保持两个主机之间的连接状态与接收指令
- 数据链接:主要负责数据传输
数据链接不是一直保持链接的,当控制链接接受到一个数据获取请求时,数据链接才会建立起来进行数据链接。
FTP 的主要命令:
- ftp 建立控制链接
- get 获取资源
- mget 获取多个资源
- put 上传文件
- mput 上传多个文件
TCP
TCP(传输控制协议)是传输层的一个重要协议,很多应用层的协议都是基于 TCP 的。TCP 是一个可靠的传输协议,它的可靠性主要来源于连接的三次握手与四次挥手
三次握手:
- 第一次:发送方发送带有 SYN=1 字段的 TCP 报文到接收方
- 第二次:接收方收到信息后发送 ACK=1 和 SYN=1 的报文返回发送方
- 第三次:发送方收到接收方的报文后,发送 ACK=1 的报文给接收方,接收方收到后,双方即建立连接成功。
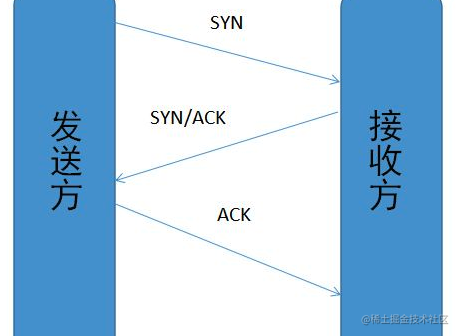
- 为什么是三次握手:因为如果是两次握手,接收方无法确定发送方是否已经收到连接报文,如果此时贸然发送数据,可能无法收到并会造成资源的浪费。
四次挥手:
-
第一次:发送方向接收方发送 FIN=1 的报文。
-
第二次:接收方收到后发送 ACK=1 的确认报文到发送方。
-
第三次:
接收方再发起一个 FIN=1 的报文到发送方。 -
第四次:发送方收到后发送一个 ACK=1 的确认报文到接收方。当报文收到后,接收方断开 TCP 连接,发送方再等待 2 个 RTT(return time)后,若接收方不再发送数据,发送方也断开 TCP 连接。
-
为什么 TCP 能保证数据的可靠传输:TCP 可以通过一系列手段来保证数据的可靠传输
- 通过报文的请求序号与接收序号,配合
滑动窗口协议和SR(重传)协议来保证报文按序接收 - 通过流量控制与拥塞控制来保证数据传输速度。
- 三次握手和四次挥手,保证数据传输双方的连接。
- 通过报文的请求序号与接收序号,配合
-
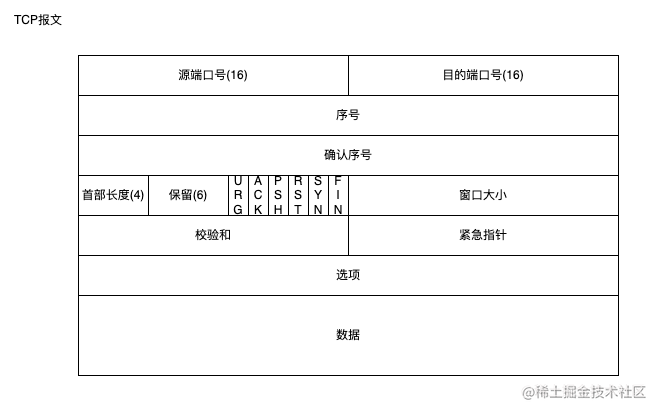
TCP 报文格式
UDP
UDP(用户数据报协议)是传输层的另一个协议,提供不可靠,无链接的数据传输。
不可靠是指不保证报文按序正确地到达,仅提供尽力的传输。
无链接指在传输数据前无需建立连接。
因为 UDP 的不可靠,无链接特性,所以它的速度比 TCP 要快得多。
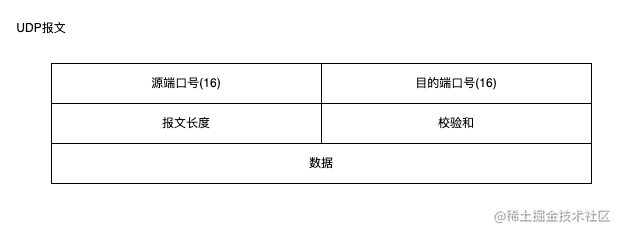
UDP 报文:
IP
IP(网络互联协议)是网络层的一个重要协议。主要是为了解决大型异构网络互联的问题和分割顶层网络应用和底层网络技术之间的耦合关系。
IP 地址由 32 个二进制位组成,每 8 个二进制位为一组,所以每组最大的长度为 255。
IP 为每台计算机都提供一个唯一的网络地址,由于当年的设计 ipv4 地址到今为止已经全部被分配完了。为了能极致地利用 IP 地址,我们把 IP 地址分为 A,B,C,D,E 5 类地址。
-
A 类地址:1.0.0.0 ~ 126.0.0.0
-
B 类地址:127.0.0.0 ~ 191.255.255.255
-
C 类地址:192.0.0.0 ~ 223.255.255.255
-
D 类地址:第一组二进制位为 1110 开头,为保留地址
-
E 类地址:以 11110 开头,也是保留地址
-
子网掩码:子网掩码主要是用来区分主机地址和网络地址。结合上面所说的五类 IP 地址,来对网络进行划分。例如,A 类地址的子网掩码是 255.0.0.0,那么代表前 8 个二进制位为主机地址,后面的 24 位都是可分配的网络地址。当然我们也可以通过子网掩码来对 A 类地址进行进一步划分。
除了将 IP 地址进行划分来合理地规划网络,还能使用地址复用技术:多台计算机共用一个 IP 地址,计算机之间组成一个内网,通过统一的收发口将数据进行发送和接收。
-
IPv6:为了彻底解决 IPv4 地址不足的问题而开发出来的 IPv6 是最有效的解决方案,IPv6 的每个地址有足足 128 个二进制位之多,基本上可以完全解决地址分配不足的问题。
但是在完全转换为 IPv6 之前的很长一段时间需要和 IPv4 共存,因为现在的部分异构网络互联设施都是以 IPv4 的标准建设的,有一部分不支持直接使用 IPv4。
为了使 IPv6 能在 IPv4 的设备上传输,可以使用以下的几种过渡技术:
- 地址翻译技术
- 双栈技术:让设备同时支持 IPv4 和 IPv6
- 隧道技术:将 IPv6 报文封装在 IPv4 报文进行传输
-
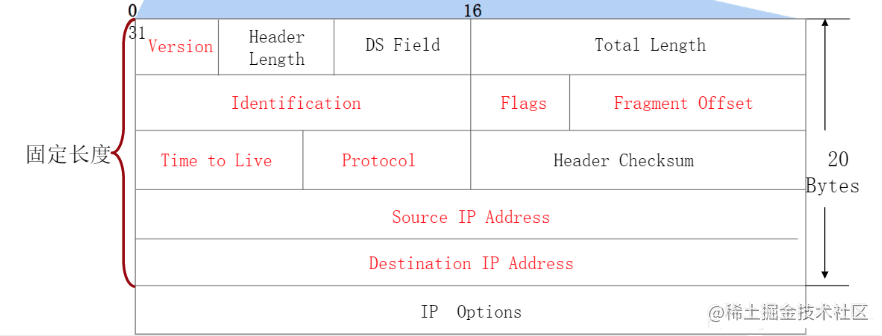
IPv4 报文结构
参考
1.MDN
2.JavaScript 高级程序设计 第 4 版
3.数据结构和算法 JavaScript 描述
4.面不面试的,你都得懂原型和原型链
5.微任务、宏任务与 Event-Loop
6.「面试题」TypeScript
7.计算机网络原理
8.How JavaScript works: Optimizing the V8 compiler for efficiency
9.小五的算法系列 - 深度优先遍历与广度优先遍历